HBase
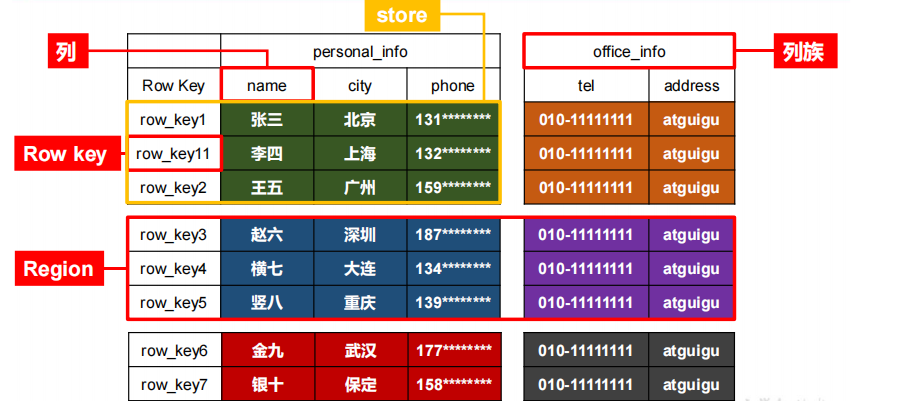
# Hbase逻辑结构
# HBase物理存储结构
# 数据模型
Name Space
命名空间,类似于关系型数据库的 DatabBase 概念,每个命名空间下有多个表。HBase有两个自带的命名空间,分别是 hbase 和 default,hbase 中存放的是 HBase 内置的表,default 表是用户默认使用的命名空间。
Region
类似于关系型数据库的表概念。不同的是,HBase 定义表时只需要声明列族即可,不需要声明具体的列。这意味着,往 HBase 写入数据时,字段可以动态、按需指定。因此,和关系型数据库相比,HBase 能够轻松应对字段变更的场景。
Row
HBase 表中的每行数据都由一个 RowKey 和多个 Column(列)组成,数据是按照 RowKey的字典顺序存储的,并且查询数据时只能根据 RowKey 进行检索,所以 RowKey 的设计十分重要。
Column
HBase 中的每个列都由 Column Family(列族)和 Column Qualifier(列限定符)进行限定,例如 info:name,info:age。建表时,只需指明列族,而列限定符无需预先定义。
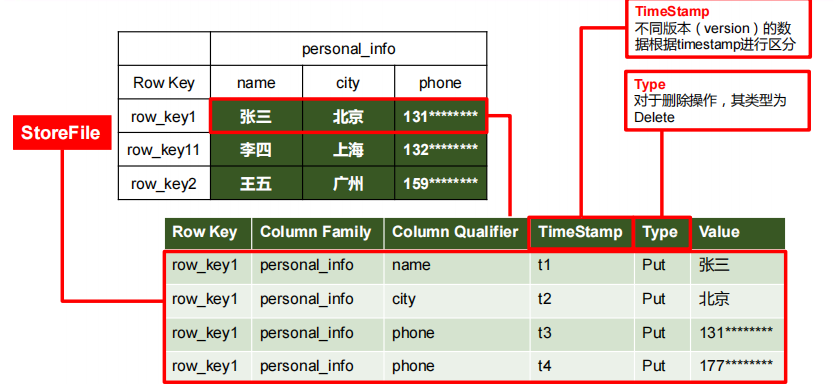
Time Stamp
用于标识数据的不同版本(version),每条数据写入时,如果不指定时间戳,系统会自动为其加上该字段,其值为写入 HBase 的时间。
Cell
由{rowkey, column Family:column Qualifier, time Stamp} 唯一确定的单元。cell 中的数据是没有类型的,全部是字节码形式存贮。
# HBase基本架构
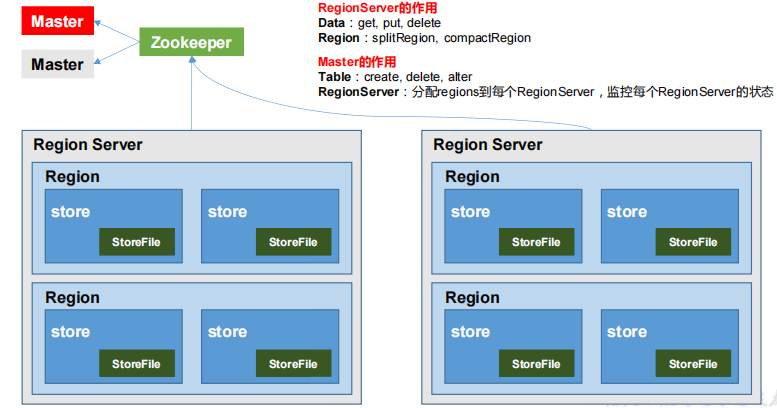
架构角色
Region Server
Region Server 为 Region 的管理者,其实现类为 HRegionServer,主要作用如下:
对于数据的操作:get, put, delete;
对于 Region 的操作:splitRegion、compactRegion。
Master
Master 是所有 Region Server 的管理者,其实现类为 HMaster,主要作用如下:
对于表的操作:create, delete, alter
对于 RegionServer的操作:分配 regions到每个RegionServer,监控每个 RegionServer的状态,负载均衡和故障转移。
Zookeeper
HBase 通过 Zookeeper 来做 Master 的高可用、RegionServer 的监控、元数据的入口以及集群配置的维护等工作。
HDFS
HDFS 为 HBase 提供最终的底层数据存储服务,同时为 HBase 提供高可用的支持。
# Hbase详细架构
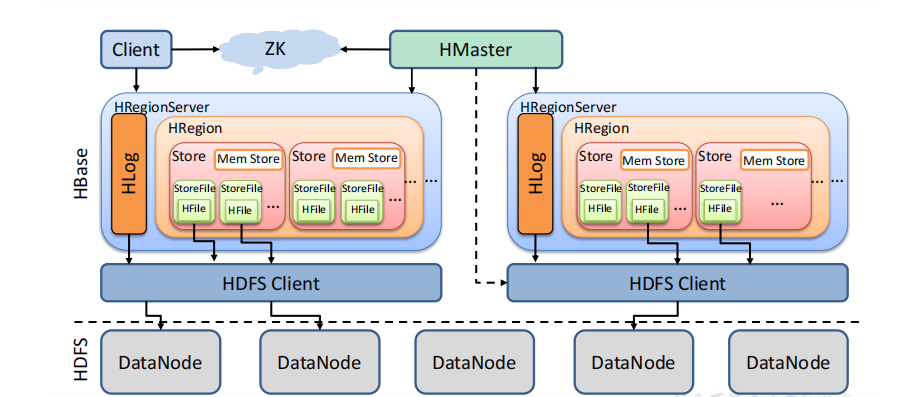
StoreFile
保存实际数据的物理文件,StoreFile 以 HFile 的形式存储在 HDFS 上。每个 Store 会有一个或多个 StoreFile(HFile),数据在每个 StoreFile 中都是有序的。
MemStore
写缓存,由于 HFile 中的数据要求是有序的,所以数据是先存储在 MemStore 中,排好序后,等到达刷写时机才会刷写到 HFile,每次刷写都会形成一个新的 HFile。
WAL
由于数据要经 MemStore 排序后才能刷写到 HFile,但把数据保存在内存中会有很高的概率导致数据丢失,为了解决这个问题,数据会先写在一个叫做 Write-Ahead logfile 的文件中,然后再写入 MemStore 中。所以在系统出现故障的时候,数据可以通过这个日志文件重建。
# 写流程

写流程
- Client 先访问 zookeeper,获取 hbase:meta 表位于哪个 Region Server。
- 访问对应的 Region Server,获取 hbase:meta 表,根据读请求的 namespace:table/rowkey,查询出目标数据位于哪个 Region Server 中的哪个 Region 中。并将该 table 的 region 信息以及 meta 表的位置信息缓存在客户端的 meta cache,方便下次访问。
- 与目标 Region Server 进行通讯
- 将数据顺序写入(追加)到 WAL
- 将数据写入对应的 MemStore,数据会在 MemStore 进行排序;
- 向客户端发送 ack;
- 等达到 MemStore 的刷写时机后,将数据刷写到 HFile。
# MemStore Flush

MemStore 刷写时机
当某个 memstroe 的大小达到了 hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size(默认值 128M), 其所在 region 的所有 memstore 都会刷写。
当 memstore 的大小达到了hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size(默认值128M) ,hbase.hregion.memstore.block.multiplier(默认值4)时,会阻止继续往该 memstore 写数据。
.当 region server 中 memstore 的总大小达到java_heapsize*hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size(默认值0.4),hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size.lower.limit(默认值0.95),region 会按照其所有 memstore 的大小顺序(由大到小)依次进行刷写。直到 region server中所有 memstore 的总大小减小到上述值以下。
当 region server 中 memstore 的总大小达到java_heapsize*hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size(默认值0.4)时,会阻止继续往所有的 memstore 写数据
到达自动刷写的时间,也会触发 memstore flush。自动刷新的时间间隔由该属性进行配置 hbase.regionserver.optionalcacheflushinterval(默认 1 小时)
# 读流程
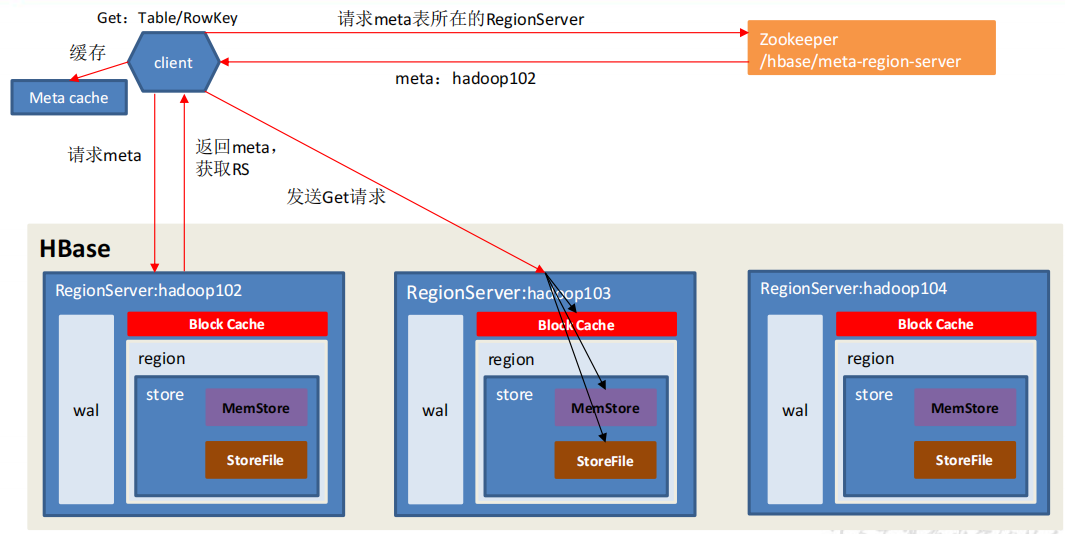
读流程
- Client 先访问 zookeeper,获取 hbase:meta 表位于哪个 Region Server。
- 访问对应的 Region Server,获取 hbase:meta 表,根据读请求的 namespace:table/rowkey,查询出目标数据位于哪个 Region Server 中的哪个 Region 中。并将该 table 的 region 信息以及 meta 表的位置信息缓存在客户端的 meta cache,方便下次访问。
- 与目标 Region Server 进行通讯;
- 分别在 Block Cache(读缓存),MemStore 和 Store File(HFile)中查询目标数据,并将查到的所有数据进行合并。此处所有数据是指同一条数据的不同版本(time stamp)或者不同的类型(Put/Delete)。
- 将从文件中查询到的数据块(Block,HFile 数据存储单元,默认大小为 64KB)缓存到Block Cache。
- 将合并后的最终结果返回给客户端。
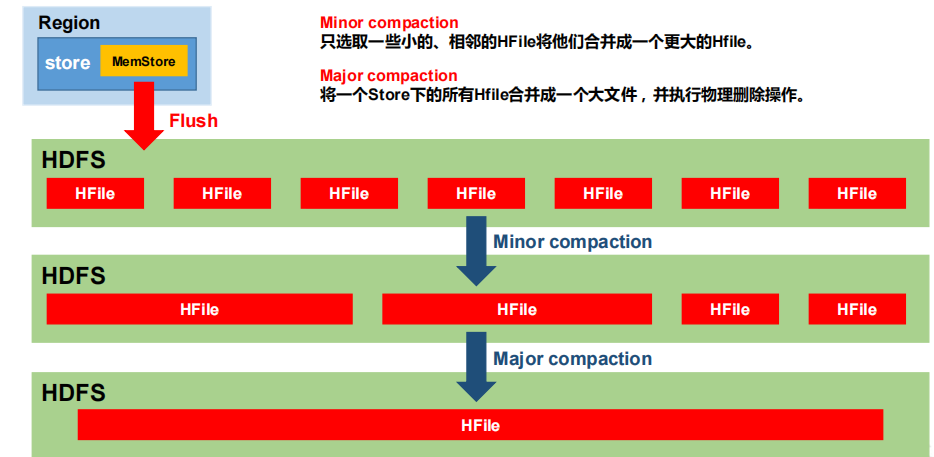
# StoreFile Compaction
由于memstore每次刷写都会生成一个新的HFile,且同一个字段的不同版本(timestamp)和不同类型(Put/Delete)有可能会分布在不同的 HFile 中,因此查询时需要遍历所有的 HFile。为了减少 HFile 的个数,以及清理掉过期和删除的数据,会进行 StoreFile Compaction。
Compaction 分为两种,分别是 Minor Compaction 和 Major Compaction。Minor Compaction会将临近的若干个较小的 HFile 合并成一个较大的 HFile,但不会清理过期和删除的数据。Major Compaction 会将一个 Store 下的所有的 HFile 合并成一个大 HFile,并且会清理掉过期
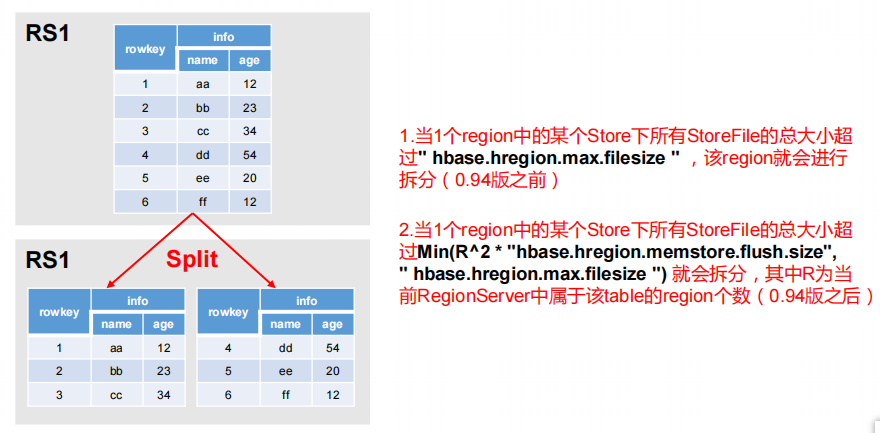
# Region Split
默认情况下,每个 Table 起初只有一个 Region,随着数据的不断写入,Region 会自动进行拆分。刚拆分时,两个子 Region 都位于当前的 Region Server,但处于负载均衡的考虑,HMaster 有可能会将某个 Region 转移给其他的 Region Server。
Region Split 时机
- 当1个region中的某个Store下所有StoreFile的总大小超过hbase.hregion.max.filesize, 该 Region 就会进行拆分(0.94 版本之前)
- 当 1 个 region 中 的 某 个 Store 下所有 StoreFile 的 总 大 小 超 过 Min(R^2 * "hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size",hbase.hregion.max.filesize"),该 Region 就会进行拆分,其中 R 为当前 Region Server 中属于该 Table 的个数(0.94 版本之后)
# MapReduce
通过 HBase 的相关 JavaAPI,我们可以实现伴随 HBase 操作的 MapReduce 过程,比如使用MapReduce 将数据从本地文件系统导入到 HBase 的表中,比如我们从 HBase 中读取一些原始数据后使用 MapReduce 做数据分析。
# 官方 HBase-MapReduce
查看HBase的MapReduce任务执行
bin/hbase mapredcp1环境变量的导入
执行环境变量的导入(临时生效,在命令行执行下述操作)
$ export HBASE_HOME=/opt/module/hbase $ export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2 $ export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=`${HBASE_HOME}/bin/hbase mapredcp`1
2
3永久生效:在/etc/profile 配置
export HBASE_HOME=/opt/module/hbase export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/module/hadoop-2.7.21
2并在 hadoop-env.sh 中配置:(注意:在 for 循环之后配)
export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$HADOOP_CLASSPATH:/opt/module/hbase/lib/*1分发重启
官方案例
统计 Student 表中有多少行数据
/opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2/bin/yarn jar lib/hbase-server-1.3.1.jar rowcounter student1使用 MapReduce 将本地数据导入到 HBase
在本地创建一个 tsv 格式的文件:fruit.tsv
1001 Apple Red 1002 Pear Yellow 1003 Pineapple Yellow1
2
3创建 Hbase 表
create 'fruit','info'1在 HDFS 中创建 input_fruit 文件夹并上传 fruit.tsv 文件
/opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /input_fruit/ /opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2/bin/hdfs dfs -put fruit.tsv /input_fruit/1
2执行 MapReduce 到 HBase 的 fruit 表中
/opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2/bin/yarn jar lib/hbase-server-1.3.1.jar importtsv \ -Dimporttsv.columns=HBASE_ROW_KEY,info:name,info:color fruit \ hdfs://hadoop102:9000/input_fruit1
2
3使用 scan 命令查看导入后的结果
scan 'fruit'1
# 自定义 HBase - MapperReducer(HDFS读取数据存储到HBase中)
Mapper编写
public class FruitMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,LongWritable, Text> { @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { context.write(key,value); } }1
2
3
4
5
6Reducer编写
public class FruitReducer extends TableReducer<LongWritable, Text, NullWritable> { @Override protected void reduce(LongWritable key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 1.遍历 100 Apple red for (Text value: values) { String[] fields = value.toString().split("\t"); Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(fields[0])); put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"),Bytes.toBytes("name"),Bytes.toBytes(fields[1])); put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"),Bytes.toBytes("color"),Bytes.toBytes(fields[2])); context.write(NullWritable.get(),put); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14Driver编写
public class FruitDriver implements Tool { Configuration configuration = null; public int run(String[] args) throws Exception { // 1.获取Job对象 Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration); // 2. 设置驱动类路径 job.setJarByClass(FruitDriver.class); // 3.设置Mapper和Mapper输出的KV类型 job.setMapperClass(FruitMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); // 4.设置Reducer类 TableMapReduceUtil.initTableReducerJob(args[1], FruitReducer.class,job); // 5.设置输入参数 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); // 6.提交任务 boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true); return res ? 0 : 1; } public void setConf(Configuration configuration) { this.configuration = configuration; } public Configuration getConf() { return configuration; } public static void main(String[] args) { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); try { int run = ToolRunner.run(conf, new FruitDriver(), args); System.exit(run); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46Package上传Jar包并运行
yarn jar bigdata_04_hbase-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar top.damoncai.hbase.c02_customer_hbase_mr.FruitDriver /fruit/fruit.tsv fruit11
# 自定义 HBase - MapperReducer2(HBase读取数据存储到HBase中)
Mapper编写
public class FruitMapper extends TableMapper<ImmutableBytesWritable, Put> { @Override protected void map(ImmutableBytesWritable key, Result value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // key就是rowkey Put put = new Put(key.get()); for (Cell cell : value.rawCells()) { put.add(cell); } context.write(key,put); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16Reducer编写
public class FruitReducer extends TableReducer<ImmutableBytesWritable, Put, NullWritable> { @Override protected void reduce(ImmutableBytesWritable key, Iterable<Put> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 1.遍历 100 Apple red for (Put put: values) { context.write(NullWritable.get(),put); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10Driver编写
public class FruitDriver implements Tool { Configuration configuration = null; public int run(String[] args) throws Exception { //得到 Configuration Configuration conf = this.getConf(); //创建 Job 任务 Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, this.getClass().getSimpleName()); job.setJarByClass(FruitDriver.class); //配置 Job Scan scan = new Scan(); scan.setCacheBlocks(false); scan.setCaching(500); //设置 Mapper,注意导入的是 mapreduce 包下的,不是 mapred 包下的,后者 是老版本 TableMapReduceUtil.initTableMapperJob( args[0], //数据源的表名 scan, //scan 扫描控制器 FruitMapper.class,//设置 Mapper 类 ImmutableBytesWritable.class,//设置 Mapper 输出 key 类型 Put.class,//设置 Mapper 输出 value 值类型 job//设置给哪个 JOB ); //设置 Reducer TableMapReduceUtil.initTableReducerJob(args[1], FruitReducer.class, job); //设置 Reduce 数量,最少 1 个 job.setNumReduceTasks(1); boolean isSuccess = job.waitForCompletion(true); if(!isSuccess){ throw new IOException("Job running with error"); } return isSuccess ? 0 : 1; } public void setConf(Configuration configuration) { this.configuration = configuration; } public Configuration getConf() { return configuration; } public static void main(String[] args) { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); try { int run = ToolRunner.run(conf, new FruitDriver(), args); System.exit(run); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55Package上传Jar包并运行
yarn jar bigdata_04_hbase-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar top.damoncai.hbase.c03_customer_hbase_mr2.FruitDriver fruit1 fruit21
# HBase MR 本地执行
Configuration使用HBase创建
public static void main(String[] args) { // Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create(); try { int run = ToolRunner.run(conf, new FruitDriver(), args); System.exit(run); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10通过源码发现需要加载hbase-site.xm文件

在resources文件夹中添加hbase-site.xml文件
# HBase与Hive集成
# 对比
Hive
Hive 的本质其实就相当于将 HDFS 中已经存储的文件在 Mysql 中做了一个双射关系,以方便使用 HQL 去管理查询。
用于数据分析、清洗(Hive 适用于离线的数据分析和清洗,延迟较高)
基于 HDFS、MapReduce,Hive 存储的数据依旧在 DataNode 上,编写的 HQL 语句终将是转换为 MapReduce 代码执行
HBase
数据库 - 是一种面向列族存储的非关系型数据库
用于存储结构化和非结构化的数据,适用于单表非关系型数据的存储,不适合做关联查询,类似 JOIN 等操作。
基于 HDFS,数据持久化存储的体现形式是 HFile,存放于 DataNode 中,被 ResionServer 以 region 的形式进行管理。
延迟较低,接入在线业务使用,面对大量的企业数据,HBase 可以直线单表大量数据的存储,同时提供了高效的数据访问速度
# HBase与Hive集成使用
HBase 与 Hive 的集成在最新的两个版本中无法兼容。所以需要重新编译
# 环境
因为我们后续可能会在操作 Hive 的同时对 HBase 也会产生影响,所以 Hive 需要持有操作HBase 的 Jar,那么接下来拷贝 Hive 所依赖的 Jar 包(或者使用软连接的形式)。
[root@ha01 hbase-1.3.1]# export HBASE_HOME=/opt/module/hbase-1.3.1
[root@ha01 hbase-1.3.1]# export HBASE_HOME=/opt/module/hive-3.1.2
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-common-1.3.1.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-common-1.3.1.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-server-1.3.1.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-server-1.3.1.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-client-1.3.1.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-client-1.3.1.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-protocol-1.3.1.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-protocol-1.3.1.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-it-1.3.1.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-it-1.3.1.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/htrace-core-3.1.0-incubating.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/htrace-core-3.1.0-incubating.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-hadoop2-compat-1.3.1.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-hadoop2-compat-1.3.1.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-hadoop-compat-1.3.1.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-hadoop-compat-1.3.1.jar
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
同时在 hive-site.xml 中修改 zookeeper 的属性,如下:
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.quorum</name>
<value>ha01.prdigital.cn,ha02.prdigital.cn,ha03.prdigital.cn</value>
<description>The list of ZooKeeper servers to talk to. This is only needed for read/write locks.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.client.port</name>
<value>2181</value>
<description>The port of ZooKeeper servers to talk to. This is only needed for read/write locks.</description>
</property>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 案例一
建立 Hive 表,关联 HBase 表,插入数据到 Hive 表的同时能够影响 HBase 表
在 Hive 中创建表同时关联 HBase
CREATE TABLE hive_hbase_emp_table( empno int, ename string, job string, mgr int, hiredate string, sal double, comm double, deptno int) STORED BY 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.hbase.HBaseStorageHandler' WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ("hbase.columns.mapping" = ":key,info:ename,info:job,info:mgr,info:hiredate,info:sal,info:co mm,info:deptno") TBLPROPERTIES ("hbase.table.name" = "hbase_emp_table");1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13完成之后,可以分别进入 Hive 和 HBase 查看,都生成了对应的表
在 Hive 中创建临时中间表,用于 load 文件中的数据
CREATE TABLE emp( empno int, ename string, job string, mgr int, hiredate string, sal double, comm double, deptno int) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10向 Hive 中间表中 load 数据
load data local inpath '/home/admin/softwares/data/emp.txt' into table emp;1通过 insert 命令将中间表中的数据导入到 Hive 关联 Hbase 的那张表中
insert into table hive_hbase_emp_table select * from emp;1查看 Hive 以及关联的 HBase 表中是否已经成功的同步插入了数据
select * from hive_hbase_emp_table; scan ‘hbase_emp_table’1
2
3
# 案例二
在 HBase 中已经存储了某一张表 hbase_emp_table,然后在 Hive 中创建一个外部表来关联 HBase 中的 hbase_emp_table 这张表,使之可以借助 Hive 来分析 HBase 这张表中的数据。
在 Hive 中创建外部表
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE relevance_hbase_emp( empno int, ename string, job string, mgr int, hiredate string, sal double, comm double, deptno int) STORED BY 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.hbase.HBaseStorageHandler' WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ("hbase.columns.mapping" = ":key,info:ename,info:job,info:mgr,info:hiredate,info:sal,info:co mm,info:deptno") TBLPROPERTIES ("hbase.table.name" = "hbase_emp_table");1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15关联后就可以使用 Hive 函数进行一些分析操作了
hive (default)> select * from relevance_hbase_emp;1
# HBase高可用
关闭HBase
bin/stop-hbase.sh1在conf目录下创建backup-masters文件
touch conf/backup-masters ha01.prdigital.cn ha02.prdigital.cn ha03.prdigital.cn1
2
3
4
5将整个conf目录scp到其他节点
xsync ../conf/1分别打开ha01,ha02,ha03 Web界面
http://ha01.prdigital.cn:16010/master-status
http://ha02.prdigital.cn:16010/master-status
http://ha03.prdigital.cn:16010/master-status

# 预分区
每一个 region 维护着 StartRow 与 EndRow,如果加入的数据符合某个 Region 维护的RowKey 范围,则该数据交给这个 Region 维护。那么依照这个原则,我们可以将数据所要投放的分区提前大致的规划好,以提高 HBase 性能。
手动设定预分区
create 'staff1','info','partition1',SPLITS => ['1000','2000','3000','4000']1生成 16 进制序列预分区
create 'staff2','info','partition2',{NUMREGIONS => 15, SPLITALGO => 'HexStringSplit'}1按照文件中设置的规则预分区
创建 splits.txt 文件内容如下:
aaaa bbbb cccc dddd1
2
3
4然后执行:
create 'staff3','partition3',SPLITS_FILE => 'splits.txt'1使用 JavaAPI 创建预分区
//自定义算法,产生一系列 hash 散列值存储在二维数组中 byte[][] splitKeys = 某个散列值函数 //创建 HbaseAdmin 实例 HBaseAdmin hAdmin = new HBaseAdmin(HbaseConfiguration.create()); //创建 HTableDescriptor 实例 HTableDescriptor tableDesc = new HTableDescriptor(tableName); //通过 HTableDescriptor 实例和散列值二维数组创建带有预分区的 Hbase 表 hAdmin.createTable(tableDesc, splitKeys);1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
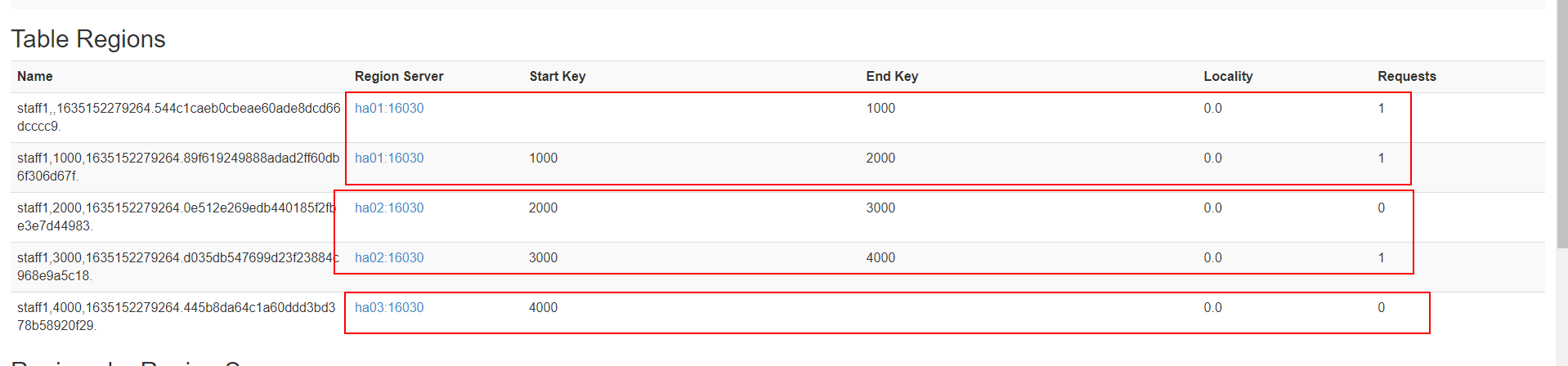
预分区的设置往往由服务器数量和数据量大小决定
- 一台服务器一般 2~3个预分区
- 数据量最好每个分区不超过10G,因为超过会自动拆分
# RowKey设计
一条数据的唯一标识就是 RowKey,那么这条数据存储于哪个分区,取决于 RowKey 处于哪个一个预分区的区间内,设计 RowKey 的主要目的 ,就是让数据均匀的分布于所有的region 中,在一定程度上防止数据倾斜。接下来我们就谈一谈 RowKey 常用的设计方案。
需要结合自身业务无设计
# 优化
# 内存优化
HBase 操作过程中需要大量的内存开销,毕竟 Table 是可以缓存在内存中的,一般会分配整个可用内存的 70%给 HBase 的 Java 堆。但是不建议分配非常大的堆内存,因为 GC 过程持续太久会导致 RegionServer 处于长期不可用状态,一般 16~48G 内存就可以了,如果因为框架占用内存过高导致系统内存不足,框架一样会被系统服务拖死。
# 基础优化
允许在 HDFS 的文件中追加内容
hdfs-site.xml、hbase-site.xml
属性:dfs.support.append 解释:开启 HDFS 追加同步,可以优秀的配合 HBase 的数据同步和持久化。默认值为 true。1
2优化 DataNode 允许的最大文件打开数
hdfs-site.xml
属性:dfs.datanode.max.transfer.threads 解释:HBase 一般都会同一时间操作大量的文件,根据集群的数量和规模以及数据动作,设置为 4096 或者更高。默认值:40961
2优化延迟高的数据操作的等待时间
hdfs-site.xml
属性:dfs.image.transfer.timeout 解释:如果对于某一次数据操作来讲,延迟非常高,socket 需要等待更长的时间,建议把该值设置为更大的值(默认 60000 毫秒),以确保 socket 不会被 timeout 掉。1
2优化数据的写入效率
mapred-site.xml
属性:mapreduce.map.output.compress mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec 解释:开启这两个数据可以大大提高文件的写入效率,减少写入时间。第一个属性值修改为true,第二个属性值修改为:org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec 或者其他压缩方式1
2
3优化 HStore 文件大小
属性:hbase.hregion.max.filesize 解释:默认值 10737418240(10GB),如果需要运行 HBase 的 MR 任务,可以减小此值,因为一个 region 对应一个 map 任务,如果单个 region 过大,会导致 map 任务执行时间过长。该值的意思就是,如果 HFile 的大小达到这个数值,则这个 region 会被切分为两个 Hfile。1
2设置 RPC 监听数量
hbase-site.xml
属性:Hbase.regionserver.handler.count 解释:默认值为 30,用于指定 RPC 监听的数量,可以根据客户端的请求数进行调整,读写请求较多时,增加此值。1
2优化 HBase 客户端缓存
hbase-site.xml
属性:hbase.client.write.buffer 解释:用于指定 Hbase 客户端缓存,增大该值可以减少 RPC 调用次数,但是会消耗更多内 存,反之则反之。一般我们需要设定一定的缓存大小,以达到减少 RPC 次数的目的。1
2
3指定 scan.next 扫描 HBase 所获取的行数
hbase-site.xml
属性:hbase.client.scanner.caching 解释:用于指定 scan.next 方法获取的默认行数,值越大,消耗内存越大。1
2flush、compact、split 机制
当 MemStore 达到阈值,将 Memstore 中的数据 Flush 进 Storefile;compact 机制则是把 flush出来的小文件合并成大的 Storefile 文件。split 则是当 Region 达到阈值,会把过大的 Region一分为二。
涉及属性:
即:128M 就是 Memstore 的默认阈值
hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size:1342177281即:这个参数的作用是当单个 HRegion 内所有的 Memstore 大小总和超过指定值时,flush该 HRegion 的所有 memstore。RegionServer 的 flush 是通过将请求添加一个队列,模拟生产消费模型来异步处理的。那这里就有一个问题,当队列来不及消费,产生大量积压请求时,可能会导致内存陡增,最坏的情况是触发 OOM。
hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit:0.4 hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.lowerLimit:0.381
2
即:当 MemStore 使用内存总量达到hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit 指定值时,将会有多个 MemStores flush 到文件中,MemStore flush 顺序是按照大小降序执行的,直到刷新到 MemStore 使用内存略小于 lowerLimit
2
